List of papers
査読付き論文
Taichi Igarashi, Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, Tomohisa Kawashima, Ken Ohsuga, Yosuke Matsumoto, and Ryoji Matsumoto 'Radiation MHD Simulations of Soft X-Ray Emitting Regions in Changing Look AGN', 2024, The Astrophysical Journal, 968, 121
Yuzhu Cui et al. 'Precessing jet nozzle connecting to a spinning black hole in M87', 2023, Nature, 621, 711
Akihiro Inoue, Ken Ohsuga, Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, Yuta Asahina, 'Modeling of Thermal Emission from ULX Pulsar Swift J0243.6+6124 with General Relativistic Radiation MHD Simulations', 2023, The Astrophysical Journal, 952, 16
Tomohisa Kawashima, Ken Ohsuga, Hiroyuki R. Takahashi 'RAIKOU (来光): A General Relativistic, Multiwavelength Radiative Transfer Code, 2023, The Astrophysical Journal, 949, 30
Kouki Nakamura, Takahiro Miyoshi, Chiho Nonaka, and Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, 'Relativistic resistive magneto-hydrodynamics code for high-energy heavy-ion collisions', 2023, The European Physical Journal C, 83, 229
Kouki Nakamura, Takahiro Miyoshi, Chiho Nonaka, and Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, 'Charge-dependent anisotropic flow in high-energy heavy-ion collisions from a relativistic resistive magneto-hydrodynamic expansion',
Kouki Nakamura, Takahiro Miyoshi, Chiho Nonaka, and Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, 'Directed flow in relativistic resistive magneto-hydrodynamic expansion for symmetric and asymmetric collision systems',
Yuh Tsunetoe, Shin Mineshige, Tomohisa Kawashima, Ken Ohsuga, Kazunori Akiyama, Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, 'Diverse Polarimetric Features of AGN Jets from Various Viewing Angles: Towards a Unified View', 2022, Galaxies, 10, 1
Jin Matsumoto, Asahina Yuta, Takiwaki Tomoya, Kotake Kei Hiroyuki R. Takahashi 'Magnetic support for neutrino-driven explosion of 3D non-rotating core-collapse supernova models', 2022, The Astrophysical Journal, 516, 1572
Yuh Tsunetoe, Shin Mineshige, Tomohisa Kawashima, Ken Ohsuga, Kazunori Akiyama, Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, 'Component of Energy Flow from Supercritical Accretion Disks Around Rotating Stellar Mass Black Holes'2022, The Astrophysical Journal, 935, 26
Yuh Tsunetoe, Shin Mineshige, Tomohisa Kawashima, Ken Ohsuga, Kazunori Akiyama, Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, 'Investigating the Disk–Jet Structure in M87 through Flux Separation in the Linear and Circular Polarization Images', 2022, The Astrophysical Journal, 931, 25
Matsumoto, Jin; Takiwaki, Tomoya; Kotake, Kei; Asahina, Yuta; Takahashi, Hiroyuki R. '2D numerical study for magnetic field dependence of neutrino-driven core-collapse supernova models', 2020, Monthly Notices of Royal Astronomical Society, 499, 4174
We investigate the origin of the soft X-ray excess component in Seyfert galaxies observed when their luminosity exceeds \( 0.1 \% \) of the Eddington luminosity (\( L_\mathrm{Edd} \)). The evolution of a dense blob in radiatively inefficient accretion ow (RIAF) is simulated by applying a radiation magnetohydrodynamic code, CANS+R. When the accretion rate onto a \( 10^7M_\odot \) black hole exceeds \( 10\% \) of the Eddington accretion rate ( \( \dot M_\mathrm{Edd} = L_\mathrm{Edd}/c^2 \) ) where \( c \) is the speed of light), the dense blob shrinks vertically because of radiative cooling and forms a Thomson thick, relatively cool ( \(\sim 10^7 \mathrm{K} \) ) region. The cool region coexists with the optically thin, hot (\( T \sim 10^{11} \mathrm{K} \) ) RIAF near the black hole. The cool disk is responsible for the soft X-ray emission, while hard X-rays are emitted from the hot inner accretion flow. Such a hybrid structure of hot and cool accretion fows is consistent with the observations of both hard and soft X-ray emissions from `changing-look' active galactic nuclei (CLAGN). Furthermore, we find that quasi-periodic oscillations (QPOs) are excited in the soft X-ray emitting region. These oscillations can be the origin of rapid X-ray time variabilities observed in CLAGN.
Taichi Igarashi, Yoshiaki Kato, Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, Ken Ohsuga, Yosuke Matsumoto, and Ryoji Matsumoto 'Radiation Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations of Sub-Eddington Accretion Flows in AGN: Origin of Soft X-ray Excess and Rapid Time Variabilities', 2020, The Astrophysical Journal, 902, 103
We study the effects of the magnetic field on the dynamics of non-rotating stellar cores by performing two-dimensional (2D), magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) simulations. To this end, we have updated our neutrino-radiation-hydrodynamics supernova code to include MHD employing a divergence cleaning method with both careful treatments of finite volume and area reconstructions. By changing the initial strength of the magnetic field, the evolution of \( 15.0, 18.4 \) and \( 27.0 M_\odot \) presupernova progenitors is investigated. An intriguing finding in our study is that the neutrino-driven explosion occurs regardless of the strength of the initial magnetic field. For the 2D models presented in this work, the neutrino heating is the main driver for the explosion, whereas the magnetic field secondary contributes to the pre-explosion dynamics. Our results show that the strong magnetic field weakens the growth of the neutrino-driven turbulence in the small scale compared to the weak magnetic field. This results in the slower increase of the turbulent kinetic energy in the postshock region, leading to the slightly delayed onset of the shock revival for models with the stronger initial magnetic field.
Yuta Asahina, Hiroyuki R. Takahashi and Ken Ohsuga 'A Numerical Scheme for General Relativistic Radiation Magnetohydrodynamics Based on Solving Grid-based Boltzmann Equation' 2020, The Astrophysical Journal, 901, 96
We investigate the properties of accretion flows on to a black hole (BH) with a mass of MBH embedded in an initially uniform gas cloud with a density of n∞ in order to study rapid growth of BHs in the early Universe. In previous work, the conditions required for super-Eddington accretion from outside the Bondi radius were studied by assuming that radiation produced at the vicinity of the central BH has a single power-law spectrum \( \nu^{-\alpha} \) at \( h\nu \geq 13.6\ \mathrm{eV} \) (\( \alpha \sim 1.5 \) ). However, radiation spectra surely depend on the BH mass and accretion rate, and determine the efficiency of radiative feedback. Here, we perform two-dimensional multifrequency radiation hydrodynamical simulations taking into account more realistic radiation spectra associated with the properties of nuclear accretion discs. We find that the critical density of gas surrounding the BH, above which transitions to super-Eddington accretion occur, is alleviated for a wide range of masses of seed BHs (\( 10 \lesssim M_\mathrm{BH}/M_\odot \lesssim 10^6 \) ) because photoionization for accretion disc spectra are less efficient than those for single power-law spectra with \( 1 \lesssim \alpha \lesssim 3 \). For disc spectra, the transition to super-Eddington is more likely to occur for lower BH masses because the radiation spectra become too hard to ionize the gas. Even when accretion flows are exposed to anisotropic radiation, the effect due to radiation spectra shrinks the ionized region and likely leads to the transition to a wholly neutral accretion phase. Finally, by generalizing our simulation results, we construct a new analytical criterion required for super-Eddington accretion; \( (M_\mathrm{BH}/10^5 M_\odot )(n_\infty/10^4\ \mathrm{cm^{−3}})\gtrsim 2.4(\left <\epsilon\right> /100\ \mathrm{eV})^{−5/9} \), where \( \left <\epsilon\right> \) is the mean energy of ionizing radiation from the central BH.
Yosuke Matsumoto, Yuta Asahina, Yuki Kudoh, Tomohisa Kawashima, Jin Matsumoto, Hiroyuki R Takahashi, Takashi Minoshima, Seiji Zenitani, Takahiro Miyoshi, Ryoji Matsumoto 'Magnetohydrodynamic simulation code CANS+: Assessments and applications', 2019, PASJ, 71, 83
We present a new magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) simulation package with the aim of providing accurate numerical solutions to astrophysical phenomena where discontinuities, shock waves, and turbulence are inherently important. The code implements the Harten-Lax-van Leer-discontinuitues (HLLD) approximate Riemann solver, the fifth-order-monotonicity-preserving interpolation (MP5) scheme, and the hyperbolic divergence cleaning method for a magnetic field. This choice of schemes has significantly improved numerical accuracy and stability, and saved computational costs in multidimensional problems. Numerical tests of one- and two-dimensional problems show the advantages of using the high-order scheme by comparing with results from a standard second-order total variation diminishing monotonic upwind scheme for conservation laws (MUSCL) scheme. The present code enables us to explore the long-term evolution of a three-dimensional accretion disk around a black hole, in which compressible MHD turbulence causes continuous mass accretion via nonlinear growth of the magneto-rotational instability (MRI). Numerical tests with various computational cell sizes exhibits a convergent picture of the early nonlinear growth of the MRI in a global model, and indicates that the MP5 scheme has more than twice the resolution of the MUSCL scheme in practical applications.
Eishun Takeo, Kohei Inayoshi, Ken Ohsuga, Hiroyuki R Takahashi, Shin Mineshige 'Super-Eddington growth of black holes in the early universe: effects of disc radiation spectra', accepted for publication in ApJ
We investigate the properties of accretion flows on to a black hole (BH) with a mass of MBH embedded in an initially uniform gas cloud with a density of n∞ in order to study rapid growth of BHs in the early Universe. In previous work, the conditions required for super-Eddington accretion from outside the Bondi radius were studied by assuming that radiation produced at the vicinity of the central BH has a single power-law spectrum \( \nu^{-\alpha} \) at \( h\nu \geq 13.6\ \mathrm{eV} \) (\( \alpha \sim 1.5 \) ). However, radiation spectra surely depend on the BH mass and accretion rate, and determine the efficiency of radiative feedback. Here, we perform two-dimensional multifrequency radiation hydrodynamical simulations taking into account more realistic radiation spectra associated with the properties of nuclear accretion discs. We find that the critical density of gas surrounding the BH, above which transitions to super-Eddington accretion occur, is alleviated for a wide range of masses of seed BHs (\( 10 \lesssim M_\mathrm{BH}/M_\odot \lesssim 10^6 \) ) because photoionization for accretion disc spectra are less efficient than those for single power-law spectra with \( 1 \lesssim \alpha \lesssim 3 \). For disc spectra, the transition to super-Eddington is more likely to occur for lower BH masses because the radiation spectra become too hard to ionize the gas. Even when accretion flows are exposed to anisotropic radiation, the effect due to radiation spectra shrinks the ionized region and likely leads to the transition to a wholly neutral accretion phase. Finally, by generalizing our simulation results, we construct a new analytical criterion required for super-Eddington accretion; \( (M_\mathrm{BH}/10^5 M_\odot )(n_\infty/10^4\ \mathrm{cm^{−3}})\gtrsim 2.4(\left <\epsilon\right> /100\ \mathrm{eV})^{−5/9} \), where \( \left <\epsilon\right> \) is the mean energy of ionizing radiation from the central BH.
Satoshi Takeshige, Hiroyuki R Takahashi, Kazunari Shibata 'Non-relativistic and relativistic magnetic reconnection with the effects of optically thin synchrotron cooling', 2019, PASJ, 71, 63
We performed special relativistic resistive magnetohydrodynamic simulations of Petscheck-type magnetic reconnection including an optically thin synchrotron cooling. The magnetization parameter, \( \sigma_0 \), which is the ratio of Poynting flux to mass flux in the upstream plasma, is taken to be 0.01 and 3. For the non-relativistic plasma ( \( \sigma_0 = 0.01 \) ), the radiative cooling subtracts thermal energy mainly in the upstream plasma and a plasma is strongly compressed at the slow shock. The cooling in the post-shock region and plasmoid also reduces the thermal energy and it forms a narrower outflow. The reconnection rate slightly increases as a result of the radiative cooling, since the plasma beta in the inflow region becomes small. The effect of decreasing thermal energy in the outflow region is more prominent for the relativistic plasma (\( \sigma_0 = 3 \) ). In this case, the outflow temperature increases and the plasma internal energy becomes comparable to the plasma rest mass energy. The subtraction of this thermal energy by radiative cooling leads to a decrease in plasma inertia and the outflows are more accelerated than without radiative cooling. The reconnection rate is also enhanced by its Lorentz contraction effect. For both non-relativistic and relativistic simulations, it is concluded that the reconnection rate is determined by the plasma beta in the inflow region.
Mariko Nomura, Tomoharu Oka, Masaya Yamada, Shunya Takekawa, Ken Ohsuga, Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, Yuta Asahina 'Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations of a Plunging Black Hole into a Molecular Cloud', 2018, accepted for the publication in ApJ
Using two-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic simulations, we investigated the gas dynamics around a black hole plunging into a molecular cloud. In these calculations, we assumed a parallel-magnetic-field layer in the cloud. The size of the accelerated region is far larger than the Bondi-Hoyle-Lyttleton radius, being approximately inversely proportional to the Alfv\'en Mach number for the plunging black hole. Our results successfully reproduce the "Y" shape in position velocity maps of the "Bullet" in the W44 molecular cloud. The size of the Bullet is also reproduced within an order of magnitude using a reasonable parameter set. This consistency supports the shooting model of the Bullet, according to which an isolated black hole plunged into a molecular cloud to form a compact broad-velocity-width feature.
Eishun Takeo, Kohei Inayoshi, Ken Ohsuga, Hiroyuki R. Takahashi and Shin Mineshige, 'Rapid growth of black holes accompanied with hot or warm outflows exposed to anisotropic super-Eddington radiation', 2018, MNRAS, 476, 673
We found that the black hole can be fed by the surrounding at the high accretion rate \(> L_{Edd}/c^2\) for the case that the radiation from the accretion disk is anisotropic. The gas falls onto the black hole from the equatorial plane, while the ionized, hot outflow is formed around the pole where the strong radiation exists.
円盤からの放射が非球対称な場合、放射が弱い領域から中性ガスが電離されずにブラックホールへと降着するため、超臨界降着が可能であることを示しました。これは円盤スケールより大きな領域から大量のガスを降着円盤に供給することが可能であることを示しており、巨大ブラックホールがガス降着によって形成されるシナリオを支持しています。
Hiroshi Kobayashi, Ken OHSUGA, Hiroyuki R. TAKAHASHI, Tomohisa KAWASHIMA, Yuta ASAHINA, Shun TAKEUCHI, and Shin MINESHIGE, 'Three-Dimensional Structure of Clumpy Outflow from Supercritical Accretion Flow onto Black Holes', 2018, PASJ, 70, 1
We found that the outflow from supercritical accretion flow is fragmentated using 3-dimensional radiation hydrodynamic simulations. We expect that the observed time variability can be explained by the light sheiding by the clumpy outflow.
超臨界降着から噴出するアウトフローはいくつものクランプに分裂することを3次元輻射流体シミュレーションで示しました。この結果は観測されるX線光度時間変動を説明出来ると考えられます。
Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, Shin Mineshige, & Ken Ohsuga 'Supercritical Accretion onto a Non-Magnetized Neutron Star: Why is it Feasible?', 2018, The Astrophysical Journal, 853, 45
We showed why supercritical accretion is feasible both onto black hole and onto neutron star using GR-RMHD simulations.
ブラックホールはエネルギーや質量を吸い込むため超臨界降着が可能ですが、(磁場が弱い)中性子星においても超臨界降着が可能であることを2.5次元一般相対論的輻射磁気流体シミュレーションにより示しました。 円盤内の輻射力はガスを吹き飛ばそうとしますが、その力は常に重力よりも弱くなるように自己制御され、さらに強いアウトフローを形成することで中性子星への降着量は実効的に低くなり、これらの結果、超臨界降着が可能となります。
図:ガス密度(左)と輻射エネルギー密度(右)。それぞれのパネルは左が中性子星、右がブラックホールへの降着。Moriyama Kotaro, Mineshige Shin, & Hiroyuki R. Takahashi 'High-frequency quasi-periodic light variations from arc-shaped gas clouds falling to a black hole', 2017, The Astrophysical Journal, 850, 56.
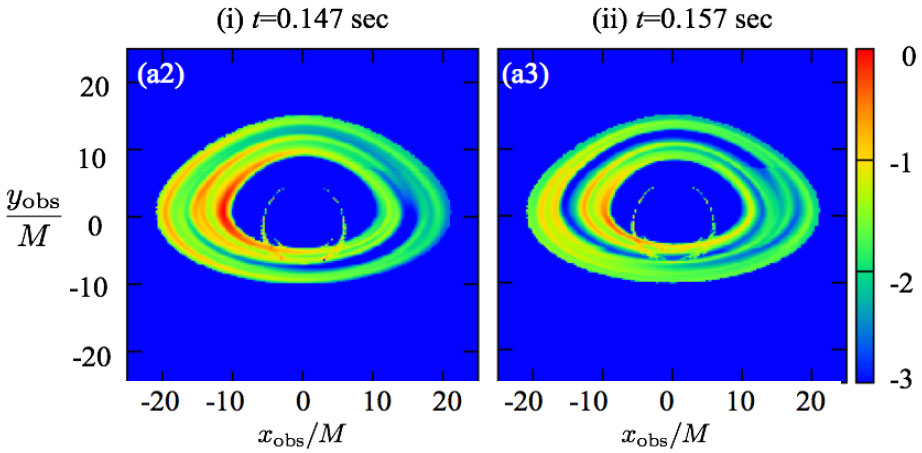 We found formation and disappearance of ring gas rotating around the black hole. The emission from this ring gas can be responsible for high frequency QPO observed in X-ray binaries.
We found formation and disappearance of ring gas rotating around the black hole. The emission from this ring gas can be responsible for high frequency QPO observed in X-ray binaries.
一般相対論的輻射磁気流体シミュレーションの結果、ブラックホール周りにリング状のガスの生成・消滅が見つかりました。このリングガスの回転周期は0.01秒で、high frequency QPOに対応すると考えられます。一方で0.08-0.1秒程度の周期も見つかり、これは円盤の乱流のタイムスケールに対応すると考えられます。
Figure: Brightness of the accretion disk (in logarizmic scale) observed with inclination angle \(i=60^\circ\). Peak (left) and dim (right) case are shown.Hiroyuki R. Takahashi & Ken Ohsuga, 'GENERAL RELATIVISTIC RADIATION MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMICS SIMULATIONS OF SUPERCRITICAL ACCRETION ONTO MAGNETIZED NEUTRON STAR; -MODELLING OF ULTRA LUMINOUS X-RAY PULSARS', 2017, The Astrophysical Journal Letter, 845, L9
We for the first time performed GR-RMHD simulations onto a magnetized neutron star. We found that the rotation period of the neutron star decreases due to the angular momentum transport from the disk gas. The spin up rate can be described by the mass accretion rate and magnetic field strength. 強磁場中性子星への超臨界降着の様子を世界で初めて一般相対論的輻射磁気流体シミュレーションにより明らかにしました。円盤と中性子星磁場の相互作用により、円盤の角運動量が中性子星へと運ばれて中性子星がspin upすること、このspin up率は降着率と磁場の単純な関数で表されることを示しました。
Figure: Color shows density (radiation energy density), arrows show velocity (radiation flux) for a left (right) panel. Blue curves show magnetic field lines and yellow curves show photosphere measured from the pole.
Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, Ken Ohsuga, Tomohisa Kawashima & Yuichiro Sekiguchi, 'Formation of Overheated Regions and Truncated Disks around Black Holes; Three-dimensional General Relativistic Radiation-magnetohydrodynamics Simulations', 2016, The Astrophysical Journal, 826, 23
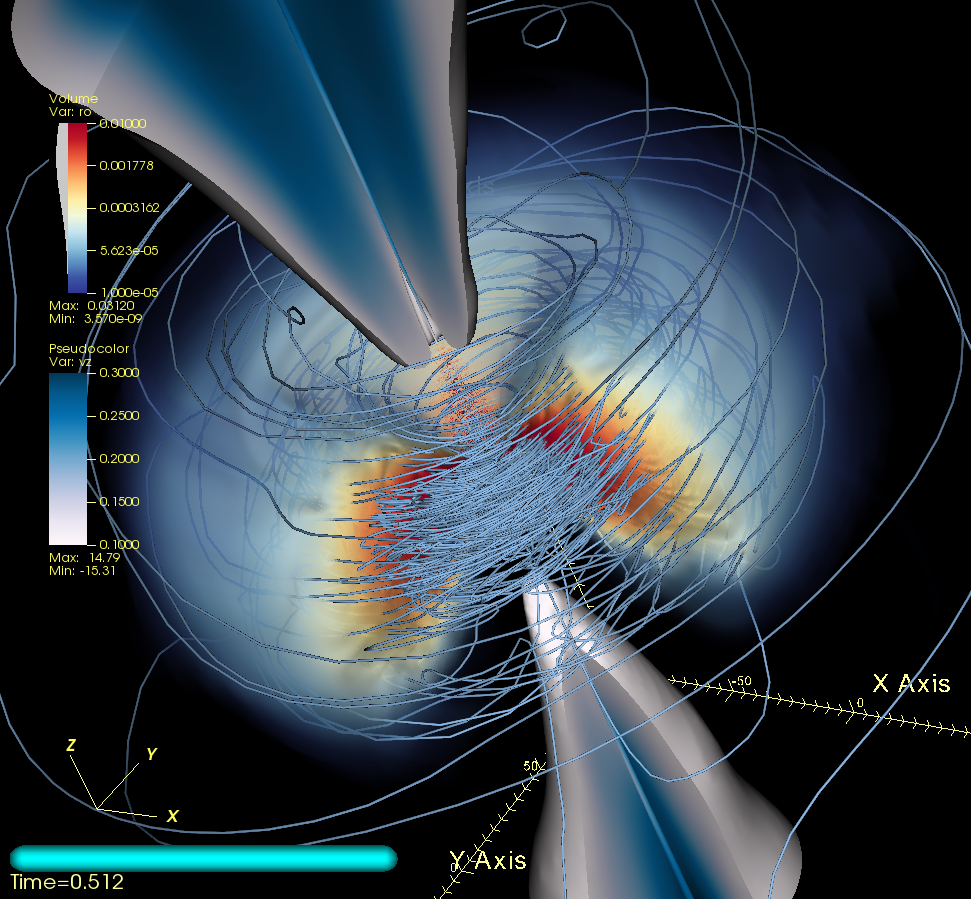 We found a formation of hot accretion flow around the black hole when the accretion rate is comparable or less than the critial accretion rate. The emitted / Comptonized photons by hot accretion flow can explain the hard X-ray spectra observed in very high state.
エディントン降着率程度でガス降着が起きると、円盤ガスの落下時間が放射冷却時間よりも短くなるために円盤は途切れ、高温のガス雲が形成されることを示しました。このモデルはVery High Stateを説明できると考えられます。
We found a formation of hot accretion flow around the black hole when the accretion rate is comparable or less than the critial accretion rate. The emitted / Comptonized photons by hot accretion flow can explain the hard X-ray spectra observed in very high state.
エディントン降着率程度でガス降着が起きると、円盤ガスの落下時間が放射冷却時間よりも短くなるために円盤は途切れ、高温のガス雲が形成されることを示しました。このモデルはVery High Stateを説明できると考えられます。
Ken Ohsuga & Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, 'A Numerical Scheme for Special Relativistic Radiation Magnetohydrodynamics Based on Solving Time-dependent Radiative Transfer Equation', 2016, ApJ, 818, 162
We develop a numerical scheme for solving the equations of fully special relativistic, radiation magnetohydrodynamics, in which the frequency-integrated, time-dependent radiation transfer equation is solved to calculate the specific intensity. This numerical scheme guarantees a conservation of energy and momentum. Adopting a semi-implicit scheme and a subtime step, the correct solution is obtained even in optically thick regime.
特殊相対論的輻射磁気流体の数値計算法、特に振動数積分した輻射輸送方程式の数値解法を提唱しました。この方法は従来の方法と異なり、エネルギー/運動量の保存が満たされます。また半陰的解法とsub-stepを用いることにより光学的に厚い状況でも大きなタイムステップを用いて正しい解に収束することを保証しています。
Mariko Nomura, Ken Ohsuga, Hiroyuki R. Takahashi & Keiichi Wada, 'Radiation Hydrodynamic Simulations of Line-Driven Disk Winds for Ultra Fast Outflows', 2016, PASJ, 68, 1616
Using 2.5-dimensional radiation hydrodynamic simulations, we investigated origins of ultra fast outflows (UFOs). We found that UFOs would exit in the wide range of black hole mass and accretion rate. The observed ratio of UFOs would be a statistical origin, i.e., it is determined by the opening angle of the outflows.
Hiroyuki R. Takahashi & Ken Ohsuga 'Radiation Drag Effects in Black Hole Outflows from Super-critical Accretion Disks via Special Relativistic Radiation Magnetohydrodynamics Simulations', 2015, PASJ, 67, 60
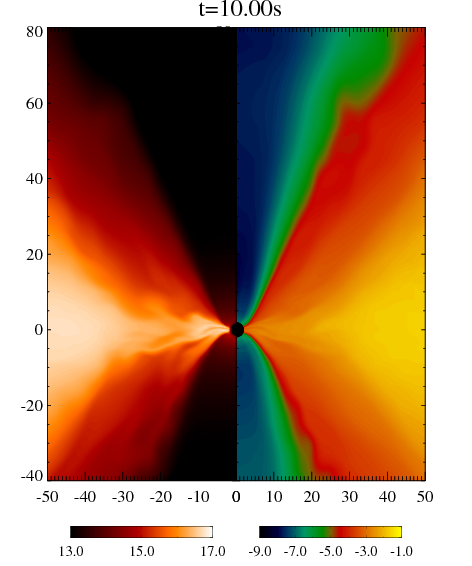 We performed 2.5-dimensional special relativistic radiation magnetohydrodynamic simulations of super-critical accretion disks.
We showed that the outflow is accelerated up to 0.4c. The terminal velocity is determined by the balance of radiation flux force and radiation drag force.
We also investigated that supper-critical accretion is possible at least \( \dot M \sim 10^4 \dot M_c \), where \( \dot M_c = L_E/c^2 \) is the critical accretion rate.
We performed 2.5-dimensional special relativistic radiation magnetohydrodynamic simulations of super-critical accretion disks.
We showed that the outflow is accelerated up to 0.4c. The terminal velocity is determined by the balance of radiation flux force and radiation drag force.
We also investigated that supper-critical accretion is possible at least \( \dot M \sim 10^4 \dot M_c \), where \( \dot M_c = L_E/c^2 \) is the critical accretion rate.
特殊相対論的輻射磁気流体コードを用いて超臨界降着円盤の大局的数値実験を行い、ジェットが輻射によって0.4c程度まで加速されること、この終端速度が輻射フラックスによる力と輻射抵抗のバランスによって決まることを示した。さらに降着率は少なくとも臨界降着の1万倍までは可能である事を示した。
Akihiro Suzuki, Hiroyuki R. Takahashi & Takahiro Kudoh 'Linear Growth of the Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability with an Adiabatic Cosmic-ray Gas', 2014, ApJ, 787, 169
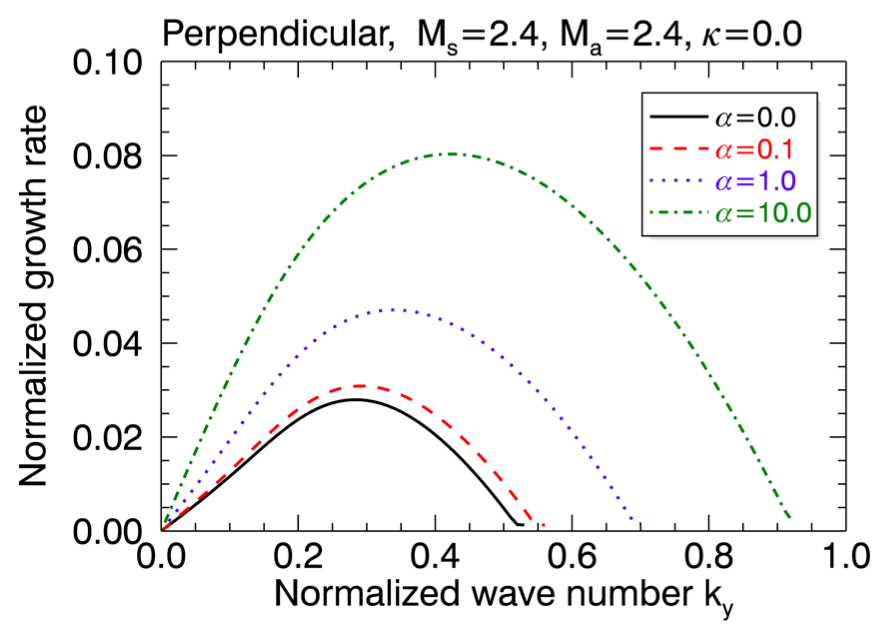 We investigate effects of cosmic-ray pressure on the linear growth of the KH instability. We found that a shear layer is more destabilized and the growth rates can be enhanced by the cosmic-ray pressure.
We investigate effects of cosmic-ray pressure on the linear growth of the KH instability. We found that a shear layer is more destabilized and the growth rates can be enhanced by the cosmic-ray pressure.
Kelvin-Helmholtz (KH) 不安定性に対する宇宙線の効果を線形解析で調べています。シアー方向に対して垂直な磁場の場合には宇宙線圧力によってKH不安定性の成長率があがること、またシアー方向に対して平行な磁場の場合には宇宙線の拡散の効果の為に垂直な場合に比べて成長率は下がる事を示しました。
Hiroyuki R. Takahashi & Ken Ohsuga, 'Numerical Treatment of Anisotropic Radiation Field Coupling with the Relativistic Resistive Magnetofluids', 2013, ApJ, 772, 127
We propose a semi-implicit scheme to solve Relativistic Resistive Radiation magnetohydrodynamics (R3MHD). We also apply our R3MHD code to relativistic magnetic reconnection problems including radiation field. We found that inflow and outflow velocities become slower due to the radiation drag force. This fact indicates that the radiation field prevents from efficien energy conversion by the magnetic reconnection when the optical depth to the electron scattering is larger than unity.
相対論的抵抗性輻射磁気流体方程式(Relativistic Resistive Radiation Magnetohydrodynamics, R3MHD)を数値的に安定に解く方法を提唱しています。また、R3MHDコードを相対論的Petschek型磁気リコネクション問題に適用し、その結果、輻射抵抗がリコネクションによるエネルギー変換を阻害することを示しています。
Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, Ken Ohsuga, Yuichiro Sekiguchi, Tsuyoshi Inoue, Kengo Tomida, 'Explicit-Implicit Scheme for Relativistic Radiation Hydrodynamics', 2013, ApJ, 764, 122
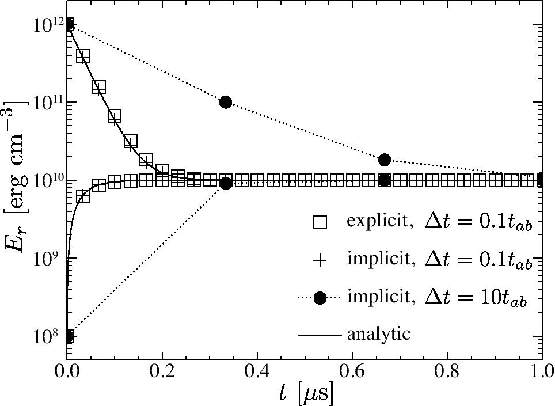 We propose an explicit-imilicit scheme for numerically solving special relativistic radiation hydrodynamic equations in the moment formalism.
We propose an explicit-imilicit scheme for numerically solving special relativistic radiation hydrodynamic equations in the moment formalism.
相対論的輻射流体方程式を数値的に安定に解く方法を提唱しています。
see also this page
Hiroyuki R. Takahashi, Takahiro Kudoh, Youhei Masada, Jin Matsumoto, 'Scaling Law of Relativistic Sweet-Parker Type Magnetic Reconnection', 2011, ApJ, 739, L53
We numerically show that the relativistic Sweet-Parker type magnetic reconnection is a slow process for energy conversion as well as that in the non-relativistic reconnection.
相対論的Sweet-Parkerリコネクションが遅いエネルギー変換である事を数値的に示しました。
Hiroyuki R.Takahashi, Eiji Asano, Ryoji Matsumoto, 'Relativistic Expansion of Magnetic Loops at the Self-similar Stage II: Magnetized outflows interacting with the ambient plasma', 2011, MNRAS, 414, 2069
 We derive the self-similar solution of relativistically expanding magnetic loops interacting with the ambient gas. The solution is numerically confirmed to be stable.
We derive the self-similar solution of relativistically expanding magnetic loops interacting with the ambient gas. The solution is numerically confirmed to be stable.
マグネターフレアに伴う膨張するループと星間ガスとの間に衝撃波を持つ自己相似解を導出し、数値的にもこの解を再現しました。
Hiroyuki R Takahashi, Kei Kotake, Nobutoshi Yasutake, 'Magnetic Field Decay due To the Wave-Particle Resonances in the Outer Crust of the Neutron Stars', 2011, ApJ, 728, 151 We show that the magnetic energy is dissipated due to the wave-particle interaction inside the outer crust of the neutron star.
中性子星内部で粒子-波相互作用によって磁気拡散が起きる事を示しました。
Hiroyuki R Takahashi, Youhei Masada ‘Stability MRI-Turbulent Accretion Disks', 2011, ApJ, 727, 106
We analytically show that disks can be destabilized to thermal, viscous, and gravitational instability due to MRI.
磁気回転不安定性の成長により、降着円盤内部で熱不安定が成長する可能性を示しました。
Hiroyuki R Takahashi, Tomoyuki Hanawa, Ryoji Matsumoto, 'Extension of the Sweet-Parker Magnetic Reconnection to the Relativistic Plasma', 2009, Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research Series, 8, 246,
We numerically show that the outflow formed in the collisionless relativistic reconnection is not accelerated up to ultra-relativistic velocity.
無衝突リコネクションにおいてバルクアウトフロー速度が相対論的にならないことを示しました。
[movie], [color]: density, [curves]: B field, [arrows]: bulk velocity
Hiroyuki R.Takahashi, Eiji Asano, Ryoji Matsumoto, 'Relativistic Expansion of Magnetic Loops at the Self-similar Stage', 2009, Monthly Notices of Royal Astronomical Society, 394, 1, 547
We derived self-similar solutions of expanding magnetic loops.
マグネターフレアに伴う磁気ループ膨張の自己相似解を導出しました。
non-refereed
thesis
[PhD Thesis] Magnetic Energy Release in Relativistically Expanding Magnetic Loops
[Bac Thesis] 万有引力定数が変化する場合の一様等方宇宙
international conference
- H. R. Takahashi
'Numerical Study of Supercritical Accretion onto Black Holes and Neutron Stars',
THE POWER OF FARADAY TOMOGRAPHY - TOWARDS 3D MAPPING OF COSMIC MAGNETIC FIELDS -
Miyazaki, Japan, May 28 - June 2, 2018
- H. R. Takahashi
'Supercritical Accretion onto Neutron Star',
DTA workshop
Mizusawa, Japan, November 8-9, 2017
- H. R. Takahashi,
‘Radiation Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations of Accretion Flows and Outflows’,
1st Asia Pacific Conference on Plasma Physics
Cheng Du, China, September 18-23, 2017 (invited)
- H. R. Takahashi,
‘General Relativistic Radiation Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations of Disk Accretion onto a Black Hole or a Neutron Star’,
Magnetic Reconnection 2017,
Ehime, Japan, March 19-23, 2017 (invited)
- H. R. Takahashi,
‘Radiation Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations of Accretion Disks',
East Asia Numerical Astrophysics Meeting,
Beijing, China,
Oct 24-28 (invited)
- H. R. Takahashi,
‘Relativistic radiation magnetohydrodynamic simulations of accretion disks ’,
International Congress on Plasma Physics,
Kaohsiung, Taipei,
June 27-July 1, 2016 (invited)
- H. R. Takahashi,
‘Accretion and Outflow in GRRMHD simulation ’,
ULXs and their environment
Strasbourg, France
June 13-16, 2016
- H. R. Takahashi,
‘3D reconnection of super-critical accretion disks in relativistic radiation magnetohydrodynamic simulations’,
Magnetic Reconnection 2016,
California, US. March 7-11, 2016 (invited)
- H. R. Takahashi, K. Ohsuga, T. Kawashima & Y. Sekiguchi
‘Relativistic Radiation Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations of Black Hole Accretion Disks and Outflows’,
Symposium on "Quarks to Universe in Computational Science (QUCS2015)",
Nov 4-8, 2015
- H. R. Takahashi, K. Ohsuga, T. Kawashima & Y. Sekiguchi
‘Numerical Study of Super Critical Accretion Disks’,
Black Hole Accretion and AGN Feedback,
Shanghai, China, Jun 1 - 6, 2015
- H. R. Takahashi, K. Ohsuga,
‘Numerical Study of Super Critical Accretion Disks’,
Plasma Conference 2014, Niigata, Japan, November 18, 2014
,
Niigata, Japan November 18 - November 21, 2014
- H. R. Takahashi, K. Ohsuga,
‘Numerical Study of Jets and Outflows from Super Critical Accretion Disks’,
ULXs - Implications for our View of the Universe
,
Leiden, Netherlands - March 31 - April 4, 2014
- H. R. Takahashi,‘Numerical Study of Jets from Supercritical Accretion Disks’,
Suzaku-MAXI 2014 Expanding the Frontiers of the X-ray Universe,
Ehime Japan, February 19 - 22 2014
- H. R. Takahashi,‘Explicit-Implicit Scheme for Relativistic Radiation Hydrodynamics’,
ASTRONUM 2013, 8th International Conference on Numerical Modeling of Space Plasma Flows,
Biarritz, France, July 1st - July 5th 2013, (invited)
- H. R. Takahashi, 'Numerical Study of Supercritical Accretion Flow onto the Black Hole Using Relativistic Radiation Magnetohydrodynamic code',
APPC12, The 12th Asia Pacific Physics Conference of AAPPS, Makuhari, Japan, July 14-19, 2013
- H. R. Takahashi,‘Magnetic Reconnection in Relativistic Plasmas’,
East Asia Numerical Astrophysics Meeting, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, October 29 - November 2, 2012
- H. R. Takahashi,‘Numerical Study of Relativistic Magnetohydrodynamic Reconnection and its Radiative Effects’,
Thirteenth Marcel Grossmann Meeting - MG13, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden, July 1-7, 2012
- H. R. Takahashi,‘Radiative MHD Simulation of Relativistic Magnetic Reconnection’,
2012 US-Japan Workshop on Magnetic Reconnection (MR2012)
Princeton, US, 2012, May 23-25 (invited)
- H. R. Takahashi, Ken Ohsuga ‘Magnetic Energy Release in Relativistic Plasma’,
IAU Symposium 279 'Death of Massive Stars: Supernovae & Gamma-Ray Bursts',
Nikko, Japan, 2012, March 12-16
- H. R. Takahashi,‘Numerical Study of Relativistic Magnetic Reconnection with R3MHD Codes’,
INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON Particles and Radiation from Cosmic Accelerators CA2012 ,
Chiba, Japan, 2012, February 20-22
- H. R. Takahashi, ‘Relativistic Magnetohydrodynamic Simulation of Magnetic Reconnection’,
Magnetic Reconnection 2010, Nara, Japan, 2010, December 5-9
- H. R. Takahashi, Y. Masada ‘Stability of MRI Turbulent Accretion Disks’, The First Year of MAXI: Monitoring variable X-ray sources - 4th international MAXI Workshop, Aoyama, Tokyo Japan, 2010, November 30 - December 2
- H. R. Takahashi, T. Kudoh, Y. Masada, J. Matsumoto ‘Relativistic Magnetohydrodynamic Simulation of Sweet-Parker type Magnetic Reconnection’, The Fourth East Asia Numerical Astrophysics Meeting (EANAM), Taipei Taiwan, 2010, November 2-5
- H. R. Takahashi, J. Matsumoto, Y. Masada, T. Kudoh ‘Numerical Study of Relativistic Magnetic Reconnection’, Deciphering the Ancient Universe with Gamma-Ray Bursts, Kyoto, Japan, 2010, April 19-23,
- H. Takahashi, T. Hanawa, R. Matsumoto ‘Requirement for the Relativistic Outflow from the Relativistic Magnetic Reconnection’, US-Japan mini-workshop on Magnetic Reconnection 2009, Princeton, USA, 2009, March 3
- H. Takahashi, T. Hanawa, R. Matsumoto ‘Extension of the Sweet-Parker Magnetic Reconnection to the Relativistic Plasma’, International Congress on Plasma Physics, Fukuoka, Japan, 2008, September 8-12
- H.Takahashi, E.Asano, T. Hanawa, R.Matsumoto, ’Magnetic Energy Release in Relativistically Expanding Magnetic Loops’, The US-Japan Workshop on Magnetic Reconnection 2008, Okinawa, Japan, March 3-6, 2008
- H.Takahashi, E.Asano, R.Matsumoto, ’Particle Acceleration by Relativistic Expansion of Magnetic Arcades’, International Conference on Astrophysics of Compact Objects, Huangshan, China, July 1-7, 2007
- H.Takahashi, E.Asano, R.Matsumoto, ’Particle Acceleration by Relativistic Expansion of Magnetic Arcades’, The Extreme Universe in the Suzaku Era, 19, Kyoto, Japan, December 4-8, 2006&
- H.Takahashi, E.Asano, R.Matsumoto, ’Particle Acceleration by Relativistic Expansion of Magnetic Arcades’, The Second East-Asia Numerical Astrophysics Meeting, Daejeon, Korea, November 1-3, 2006
- H.Takahashi, E.Asano, R.Matsumoto, ‘Particle Acceleration by Relativistic Expansion of Magnetic Arcades’, XXVIth IAU GA Joint Discussion, Cosmic Particle Acceleration From Solar System to AGNs, 01-17, Prague, Czech Republic, 2006, 8.17
- E.Asano, - H.Takahashi, R.Matsumoto, ‘Numerical Simulation of Relativistic Expansion of Magnetic Arcades in Magnetars’, The Second East-Asia Numerical Astrophysics Meeting, Daejeon, Korea, November 1-3, 2006
国内発表リスト
- 高橋博之、大須賀健、小川拓未
'振動数依存型輻射磁気流体シミュレーションコードの開発'
日本天文学会2018春期年会
千葉、2018年3月14日-17日
- 高橋博之
'振動数依存型輻射モーメント式の数値解法'
ブラックホール降着流ミニワークショップ
千葉、2018年3月5日-6日
- 高橋博之
'降着円盤の輻射磁気流体シミュレーション'
素粒子・原子核・宇宙「京からポスト京に向けて」シンポジウム
東京、2017年12月28日
- 高橋博之
'超臨界降着の一般相対論的輻射磁気流体シミュレーション'
嶺重グループOB研究会
有馬、2017年12月16日
- 高橋博之
'中性子星への超臨界降着現象'
CfCAユーザーズミーティング
三鷹、2017年11月28日-29日
- 高橋 博之
'中性子星と超臨界降着円盤',
中性子星の観測と理論
三鷹、2017年11月23-25日
- 高橋 博之
'一般相対論的輻射磁気流体計算による中性子星への超臨界降着とアウトフロー 形成機構',
日本天文学会秋期年会
札幌、2017年9月11-13日
- 高橋 博之
'中性子星への超臨界降着は可能か?',
日本天文学会秋期年会
札幌、2017年9月11-13日
- 高橋 博之
'宇宙プラズマシミュレーション'
第56回プラズマ若手夏の学校 夏期セミナー
赤穂, 2017年8月30日(invited)
- 高橋 博之
'中性子星への超臨界降着の一般相対
論的輻射磁気流体シミュレーション',
磁気流体プラズマで探る高エネルギー天体現象研究会
東京、2017年8月28-30日
- 高橋 博之
'双極子磁場を持つ中性子星への超臨界降着の一般相対論的輻射磁気流体シミュレーション',
日本天文学会春季年会、
九州大学、2017年3月15-18日
- 高橋 博之
'Black Hole and Neutron Star Accretion',
Ultra-Luminous X-ray Source研究会 - 多波長で探る降着系の統一描像
相模原、2017年3月 (invited)
- 高橋 博之
'ブラックホール・中性子星降着円盤とアウトフロー',
理論懇シンポジウム 第29回
相模原、2016年12月 (invited)
- 高橋 博之
'輻射磁気流体シミュレーションによる降着円盤とアウトフロー研究',
高エネルギー宇宙物理学研究会
相模原、2016年11月 (invited)
- 高橋 博之
'弱磁場中性子星への超臨界降の一般相対論的輻射磁気流体シミュレーション',
CfCAユーザーズミーティング
三鷹、2016年11月29日-30日
- 高橋 博之
'弱磁場中性子星への超臨界降の一般相対論的輻射磁気流体シミュレーション',
日本流体力学会
金沢、2016年9月26日-28日
- 高橋 博之
'降着円盤の輻射磁気流体シミュレーション',
日本物理学会2016秋期年会
金沢、2016年9月 (invited)
- 高橋 博之
'相対論的輻射磁気流体シミュレーションで探るブラックホール降着円盤の活動性',
現象論解析セミナー第9回
茨城大学、2016年3月20日-21日 (invited)
- 高橋 博之
'一般相対論的輻射磁気流体による超臨界降着円盤シミュレーション',
日本天文学会春季年会
首都大学東京、2016年3月14日-17日 (invited)
- 高橋 博之
'一般相対論的輻射磁気流体による降着円盤シミュレーション',
CfCAユーザーズミーティング
岩手、2016年1月28日-29日
- 高橋 博之
'ブラックホール周りにおける高温ガス雲形成の一般相対論的輻射磁気流体シミュレーション ',
第28回理論懇シンポジウム
大阪大学、2015年12月23日-25日
- 高橋 博之
'超臨界降着円盤の円盤構造'
,
流体力学会年会2015
東京工業大学、2015年9月26日
- 高橋 博之
'一般相対論的輻射磁気流体計算による円盤コロナの形成について'
,
日本天文学会秋季年会
,
甲南大学、2015年9月10日
- 高橋 博之
'恒星質量ブラックホール降着円盤シミュレーション研究の現状'
,
超巨大ブラックホール降着円盤スペクトルの解釈を巡って
,
宇宙航空研究開発機構(JAXA)淵野辺キャンパス、2015年8月10日 - 11日, (invited)
- 高橋 博之
'高エネルギー天文学、特に降着円盤における輻射過程とシミュレーション研究の現状'
, Solar-C時代の太陽研究
,
国立天文台、2015年7月3日, (invited)
- 高橋 博之、
'一般相対論的輻射磁気流体計算で探る高降着率円盤構造'、
,
日本天文学会春期年会
、大阪大学、2015年3月21日
- 高橋 博之、
'ブラックホール降着円盤の3次元一般相対論的輻射磁気流体シミュレーション'
,
第27回理論懇シンポジウム 「理論天文学/宇宙物理学と境界領域」
、国立天文台、2014年12月23日-12月26日
- 高橋 博之、大須賀健、
'超臨界降着円盤の一般相対論的輻射磁気流体シミュレーション'
,
日本天文学会秋季年会
、山形大学、2014年9月11日
- 高橋 博之、
'Relativistic Magnetic Reconnection'
,
超新星/ガンマ線バースト研究会2014
、理化学研究所、2014年8月25日-27日 (invited)
- 高橋 博之、'超臨界降着流からのアウトフロー 〜ブラックホールまわりでの放射の輸送と相対論的な磁気リコネクション'、
第7回ブラックホール磁気圏勉強会、熊本大学、2014年3月3日-5日 (invited)
- 高橋 博之、'相対論的抵抗性輻射磁気流体コードの開発'、
STEシミュレーション研究会 & 太陽地球惑星系科学(STP)シミュレーション・モデリング技法勉強会 合同研究集会 - 宇宙プラズマ・大気・天体 -、九州大学情報基盤研究開発センター、2013年12月23日-27日 (invited)
- 高橋 博之、
'超臨界降着からのアウトフロー形成'、
日本流体力学会年会2013
、東京農工大学、2013年9月13日
- 高橋 博之、
'超臨界降着流からのジェット/アウトフローの形成'
、日本天文学会秋期年会
、東北大学、2013年9月12日
- 高橋 博之、'超臨界降着流からの放射とアウトフローの形成'、
HPCI戦略プログラム分野5'物質と宇宙の起源と構造'全体シンポジウム
- 高橋 博之、'モーメント法における相対論的輻射磁気流体の半陰的解法'、
宇宙磁気流体・プラズマシミュレーションワークショップ WS2013
- 高橋 博之、'相対論的散逸性磁気流体シミュレーション'、
理論天文学宇宙物理学懇談会シンポジウム
'計算宇宙物理学の新展開'、つくばエポカル、2012年12月22日-24日(invited)
-高橋 博之、'相対論的輻射(磁気)流体力学'、宇宙磁気流体・プラズマシミュレーションサマースクール、千葉大学アカデミックリンクセンター、総合校舎、2012年8月6日-10日(演習担当)
- 高橋 博之、'相対論的抵抗性輻射磁気流体コードの開発とその応用'、
日本天文学会春期年会、
龍谷大学、2012年3月19日-22日
- 高橋 博之、"相対論的磁気リコネクションによるエネルギー解放と輻射による影響"、
HPCI戦略プログラム分野5'物質と宇宙の起源と構造'全体シンポジウム、
秋葉原コンベンションホール、2012年3月8日
- 高橋 博之、"モーメント法を用いた輻射場と相対論的磁気流体の数値解法"、
宇宙磁気流体・プラズマシミュレーションワークショップ WS2012
千葉大学, 2012年3月6日
- 高橋 博之、"相対論的抵抗性輻射磁気流体方程式の数値解法と相対論的磁気リコネクション問題への応用",
第五回ブラックホール磁気圏勉強会,
名古屋大学 2012年2月28日-3月1日 (invited)
- 高橋 博之、'相対論的リコネクションと輻射場による影響',
NINS/UT Reconnection Workshop 2012,
東京都千代田区一ツ橋 学術総合センター 2F 中会議場4, 2012年2月19日-20日 (invited)
- 高橋 博之、'相対論的MHDリコネクションの輻射による影響'、
CfCA ユーザーズミーティング、
O5、国立天文台三鷹、2011年1月17日
- 高橋 博之、'R3MHD(相対論+電気抵抗+輻射+磁気流体)方程式の数値解法'、
SGEPSS波動分科会'一般相対論とMHDプラズマ',
福井県武生市府中町屋倶楽部, 2011年12月16日-17日(invited)
- 高橋 博之、'Beyond the Relativistic Magnetohydrodynamics: Numerical Scheme for Relativistic Resistive Radiation Hydrodynamics'、
Plasma Conference 2011、 24P155-R、石川県立音楽堂、2011年11月24日
- 高橋 博之、'磁気リコネクションでフレアを説明できるか?' 、AGN-JET WORKSHOP 2011 -他波長放射で探る活動銀河核ジェット-、国立天文台、2011年9月26日-28日
- 高橋 博之、'陰的解法に基づく安定な相対論的輻射磁気流体コードの開発' 、日本天文学会秋期年会、J37a、鹿児島大学、2011年9月20日
- 高橋 博之、'陽・陰解法を用いた相対論的輻射磁気流体コードの開発'、流体力学会、1F34、 都立大学、2011年9月7日
- 高橋 博之、'相対論的磁気流体+αシミュレーション 〜輻射磁気流体編〜' 、千葉大学科研費打ち合わせ、千葉大学、2011年3月11日
- 高橋 博之、'磁気リコネクションにおける相対論と非相対論的プラズマでの違い' 、第4回ブラックホ−ル磁気圏勉強会、大同大学、2011年3月1日
- 高橋 博之、'CfCAキューを用いた研究成果' 、2010年度CfCAユーザーズミーティング、国立天文台三鷹、2011年1月12日
- 高橋 博之、'相対論的磁気リコネクションは速いエネルギー変換機構か?'名古屋大学Ta研セミナー、名古屋大学、2010年11月26日
- 高橋 博之、松本仁、政田洋平、工藤哲洋'相対論的Sweet-Parker型磁気リコネクションの数値的研究'、日本流体学会年会2010、宇宙・惑星(1), 北海道大学、2010年9月10日
- 高橋 博之、'相対論的MHDリコネクションの数値的研究'、千葉大学科研費打ち合わせ、千葉大学、2010年8月30日
- 高橋 博之、政田洋平'磁気回転不安定性を考慮した降着円盤モデル'、2010年春期天文学会春期年会、J14a, 広島大学、2010年3月25日
- 高橋 博之、松本仁、政田洋平、工藤哲洋'近似リーマン解法を用いた相対論的散逸性磁気流体方程式の解法'、2010年春期天文学会春期年会、J15b, 広島大学、2010年3月25日
- 高橋 博之'近似リーマン解法を用いた相対論的Sweet-Parker型磁気リコネクションシミュレーション'、第三回ブラックホール磁気圏勉強会、大阪市立大学、2010年3月2日
- 高橋 博之'相対論的MHDシミュレーションについての議論'、千葉大学科研費打ち合わせ、千葉大学、2010年2月22日
- 高橋 博之、'相対論的散逸性磁気流体方程式の近似リーマン解法'、千葉大学セミナー、千葉大学、2010年2月5日
- 高橋 博之、政田洋平 '磁気回転不安定性が成長した降着円盤の構造'、第22回理論懇シンポジウム、42、名古屋大学2009年12月20日-22日
- 高橋 博之 'マグネターフレアと磁気散逸機構'、京都大学セミナー、京都大学、2009年11月18日
- 高橋 博之 '磁気圧によって駆動された相対論的速度を持つ磁気ループの自己相似的成長'、日本天文学会2009年度秋期年会、J42b、 山口大学、2009年9月15日
- 高橋 博之 '相対論的磁気再結合によるアウトフロー加速と粒子加速'、早稲田大学セミナー、早稲田大学、2009年7月3日
- 高橋 博之、花輪 知幸、松元 亮治、'磁気再結合から相対論的アウトフローが生成される条件'、第9回高宇連研究会'宇宙ジェットの多様性と普遍性'、愛媛大学、2009年3月16-18日
- 高橋 博之、'相対論的磁気リコネクションにおける相対論的アウトフロー生成の可能性について'、第21回理論懇シンポジウム、国立天文台、2008年12月17日
- 高橋 博之、花輪 知幸、松元 亮治、'Sweet-Parker型磁気リコネクションの相対論的プラズマへの拡張'、日本天文学会2008年度春季年会、J52a、国立オリンピック記念青少年総合センター 2008年3月27日
- 高橋 博之、浅野 栄治、松元 亮治、'トロイダル磁場を持つ相対論的に膨張する磁気ループの自己相似解'、日本天文学会2007年度秋季年会、J148a、岐阜大学 2007年9月28日
- 高橋 博之、浅野 栄治、松元 亮治、'膨張する磁気アーケードにおける粒子加速の相対論的PICシミュレーション'、日本天文学会2007年度春季年会、J20a、東海大学 2007年3月29日
- 高橋 博之、浅野 栄治、松元 亮治、'相対論的に膨張する磁気アーケードと粒子加速について'、千葉大学総合メディア基盤センター研究会、千葉大学 2007年3月16日
- 高橋 博之、浅野 栄治、松元 亮治、'相対論的に膨張する磁気アーケード中と粒子加速の理論'、高エネルギー天体現象と粒子加速の理論、大阪大学 2006年11月10日
- 高橋 博之、浅野 栄治、松元 亮治、'相対論的磁気アーケード中での粒子加速'、磁気リコネクションワークショップ、安保ホール(名古屋) 2006年10月4日
- 高橋 博之、浅野 栄治, 松元 亮治、'相対論的磁気アーケードの膨張と粒子加速', 日本物理学会 2006年度秋期年会 領域2 プラズマ宇宙物理、 24pQB 11、千葉大学 2006年9月24日
- 高橋 博之、浅野 栄治, 松元 亮治、'相対論的に膨張する磁気アーケード中での粒子加速', 日本天文学会 2006年度秋期年会、J54a, 九州国際大学 2006年9月21日
- 高橋 博之、浅野 栄治、松元 亮治、'相対論的磁気アーケード中における粒子加速'、日本地球惑星科学連合2006年大会、U054-006、幕張メッセ 2006年5月14日
- 浅野 栄治、- 高橋 博之、松元 亮治、'相対論的に膨張する磁気アーケード膨張とプラズモイド噴出の数値実験'、日本天文学会 2006年度秋期年会、J53a、九州国際大学 2006年9月21日 口頭発表
- 浅野 栄治、- 高橋 博之、松元 亮治、'中性子星磁気圏から噴出する相対論的磁気タワージェットの数値実験'、日本天文学会2007年度春季年会、J19a、東海大学 2007年3月29日
- 浅野 栄治、- 高橋 博之、松元 亮治、'相対論的磁気タワージェットの数値実験'、すざく時代のブラックホール天文学、京都大学 2007年3月13日〜15日
紀要・その他
-
'降着円盤入門' 「プラズマ若手夏の学校 核融合炉夏期セミナー 2017」の講義資料
-
'計算科学ロードマップ2017' の一部を執筆, 2017年
-
'計算科学ロードマップ' の一部を執筆, 2014年
-
銭谷誠司、高橋博之、 '新たなリコネクション研究の芽、相対論領域のリコネクション', 2013, Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research, 89, 12, 845-848
-
松元亮治、高橋博之、 'リコネクション研究の課題と将来、高エネルギー宇宙物理学分野の課題と将来', 2013, Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research, 89, 12, 864-867
-
高橋博之、 'モーメント法を用いた相対論的輻射流体の数値解法', 宇宙磁気流体・プラズマシミュレーションワークショップ --WS2012--, 数値天文学マニュアル第4章
一般講演
-
NHKスペシャル「スペース・スペクタクル」 第2集 見えた!ブラックホールの謎 取材協力、2019年7月28日
-
高橋博之、'時空の果て ブラックホール' 朝日カルチャーセンター横浜教室、横浜、2018年6月30日
-
高橋博之、'ブラックホールが生み出す光りと風' 全国同時七夕講演会「宇宙の風に吹かれて」筑波技術大学、2017年8月6日
-
高橋博之、'ブラックホールを観る' 朝物理勉強会、東京、2016年2月13日
-
高橋博之、'光り輝くブラックホール' 朝日カルチャーセンター横浜教室、横浜、2015年11月23日
-
高橋博之、'超大質量ブラックホールはいかにして作られたのか - 定説を覆す急成長の謎にせまる' 月刊JICFuS、2015年4月13日